programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/43162
코딩테스트 연습 - 네트워크
네트워크란 컴퓨터 상호 간에 정보를 교환할 수 있도록 연결된 형태를 의미합니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 B가 직접적으로 연결되어있고, 컴퓨터 B와 컴퓨터 C가 직접적으로 연결되어 있
programmers.co.kr
네트워크란 컴퓨터 상호 간에 정보를 교환할 수 있도록 연결된 형태를 의미합니다. 예를 들어, 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 B가 직접적으로 연결되어있고, 컴퓨터 B와 컴퓨터 C가 직접적으로 연결되어 있을 때 컴퓨터 A와 컴퓨터 C도 간접적으로 연결되어 정보를 교환할 수 있습니다. 따라서 컴퓨터 A, B, C는 모두 같은 네트워크 상에 있다고 할 수 있습니다.
컴퓨터의 개수 n, 연결에 대한 정보가 담긴 2차원 배열 computers가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 네트워크의 개수를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성하시오.
제한사항
- 컴퓨터의 개수 n은 1 이상 200 이하인 자연수입니다.
- 각 컴퓨터는 0부터 n-1인 정수로 표현합니다.
- i번 컴퓨터와 j번 컴퓨터가 연결되어 있으면 computers[i][j]를 1로 표현합니다.
- computer[i][i]는 항상 1입니다.
입출력 예
ncomputersreturn
| 3 | [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]] | 2 |
| 3 | [[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]] | 1 |
입출력 예 설명
예제 #1
아래와 같이 2개의 네트워크가 있습니다.
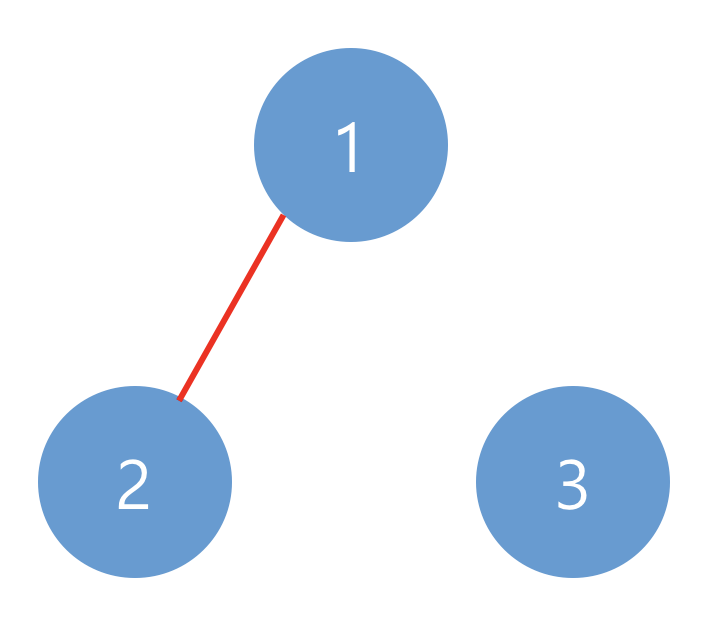
예제 #2
아래와 같이 1개의 네트워크가 있습니다.
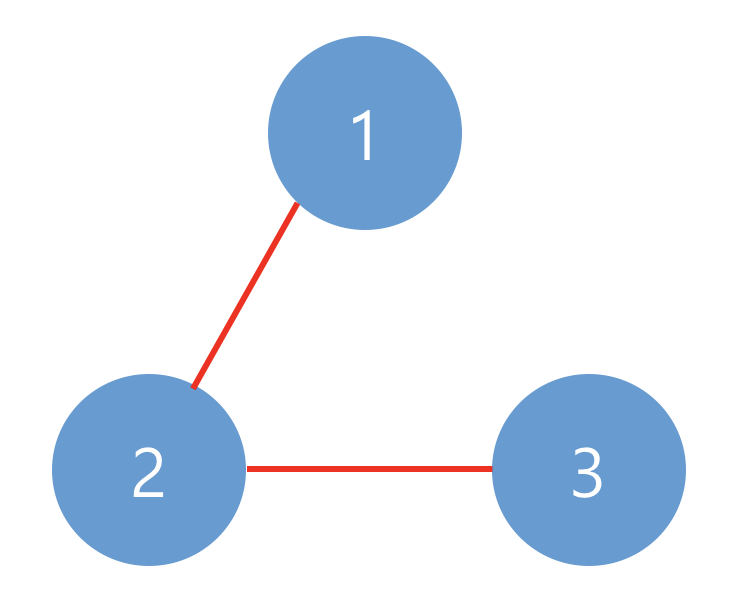
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<bool> isVisited;
bool dfs(int index, vector<vector<int>> computers)
{
if(isVisited[index])
{
return false;
}
isVisited[index] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < computers.size(); i++)
{
if(computers[index][i] == 1)
{
dfs(i, computers);
}
}
return true;
}
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> computers) {
int answer = 0;
isVisited.assign(computers.size(),false);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(dfs(i, computers))
{
answer += 1;
}
}
return answer;
}DFS 깊이 탐색 방식
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> parent;
void make( int _n )
{
parent = vector<int>(_n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= _n; i++)
{
parent[i] = i;
}
}
int Find(int _x)
{
if ( parent[_x] != _x )
{
parent[_x] = Find( parent[_x] );
}
return parent[_x];
}
void Union( int _x, int _y )
{
int root1 = Find(_x);
int root2 = Find(_y);
parent[root1] = root2;
}
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> computers)
{
int answer = 0, len = computers.size();
make(n);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0; j < len; j++ )
{
if ( i == j ) continue;
if (computers[i][j] == 1)
{
Union( i + 1, j + 1 );
}
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= len; i++ )
{
if ( parent[i] == i )
{
answer++;
}
}
return answer;
}Union Find 방식
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> computers)
{
int answer = 0;
queue<int> q;
bool* visited = new bool[n + 1];
memset(visited, false, n + 1);
for (int j = 0; j < computers.size(); j++)
{
q.push(j);
if (!visited[j])
{
visited[j] = true;
answer++;
}
while (!q.empty())
{
int temp = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < computers[temp].size(); i++)
{
if (temp == i) continue;
if (!visited[i])
{
if (computers[temp][i] == 1)
{
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
return answer;
}
int main()
{
cin.tie(NULL);
cin.sync_with_stdio(false);
int n=3;
vector<vector<int>> computers;
vector<int> computer;
//[[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 1]]
//[[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 1]]
computer.push_back(1);
computer.push_back(1);
computer.push_back(0);
computers.push_back(computer);
computer.clear();
computer.push_back(1);
computer.push_back(1);
computer.push_back(1);
computers.push_back(computer);
computer.clear();
computer.push_back(0);
computer.push_back(1);
computer.push_back(1);
computers.push_back(computer);
computer.clear();
cout<<"answer : " << solution(n, computers) << "\n";
}
BFS
'프로그래머스 > 3 단계' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ 프로그래머스 3 단계 ] 입국심사 (0) | 2021.05.13 |
|---|---|
| [ 프로그래머스 3 단계 ] 단속카메라 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| [ 프로그래머스 3 단계 ] 디스크 컨트롤러 (0) | 2021.04.26 |
| [ 프로그래머스 3 단계 ] 정수 삼각형 (0) | 2021.04.08 |







